Java中的接口和继承
- 2022-10-14 10:35:12
- 2188次 动力节点
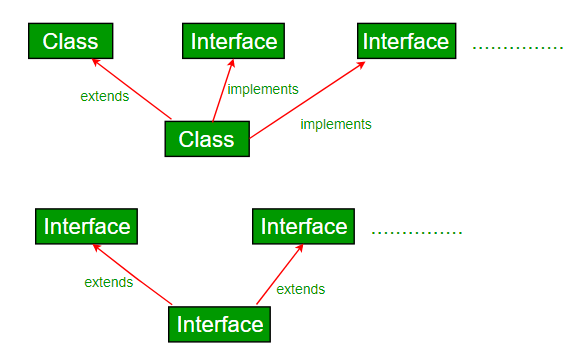
相信大家对Java继承定义已经有所了解,先决条件: Java、Java 和多重继承中的接口一个类可以扩展另一个类和/可以实现一个和多个接口。
例子:
// Java program to demonstrate that a class can
// implement multiple interfaces
import java.io.*;
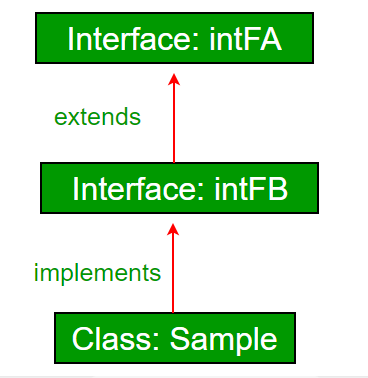
interface intfA
{
void m1();
}
interface intfB
{
void m2();
}
// class implements both interfaces
// and provides implementation to the method.
class sample implements intfA, intfB
{
@Override
public void m1()
{
System.out.println("Welcome: inside the method m1");
}
@Override
public void m2()
{
System.out.println("Welcome: inside the method m2");
}
}
class GFG
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
sample ob1 = new sample();
// calling the method implemented
// within the class.
ob1.m1();
ob1.m2();
}
}
输出;
欢迎:在方法m1里面
欢迎:在方法m2里面
继承就是将父类的属性继承到子类中。
Java 中的继承是一种机制,其中一个对象获取父对象的所有属性和行为。
Java 继承背后的理念是,您可以创建基于现有类的新类。从现有类继承时,可以重用父类的方法和字段。
您还可以在当前类中添加新方法和字段。
继承表示 IS_A 关系,也称为父子关系。
例如:
狗 IS_A 动物
车 IS_A 车辆
员工 IS_A 人
外科医生 IS_A 医生等。
class Animal
{
public void eat()
{
}
}
Class Dog extends Animal
{
Public static void main(String args[])
{
Dog d=new Dog;
d.eat();
}
}
Java继承的语法
类 <子类名称> 扩展 <超类名称>
{
//方法和字段
}
注意:extends 关键字表示您正在创建一个从现有类派生的新类。“扩展”的意思是增加功能。
例如_1:
import java.io.*;
class Person {
int id;
String name;
void set_Person()
{
try{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter the Id:");
id=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("Enter the Name");
name=br.readLine();
}catch(Exception ex){ex.printStackTrace();}
}
void disp_Person()
{
System.out.print(id+" "+name+" ");
}
}
class Employee extends Person{
int sal;
String desgn;
void set_Emp()
{
try{
set_Person();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Enter the Designation:");
desgn=br.readLine();
System.out.println("Enter the Salary:");
sal=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
}catch(Exception ex){ex.printStackTrace();}
}
void disp_Emp()
{
disp_Person();
System.out.println(desgn+" "+sal);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Employee e1=new Employee();
e1.set_Emp();
e1.disp_Emp();
}
}
例如_2:
class Person1 {
int id;
String name;
void set_Person(int id,String name)
{
try{
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}catch(Exception ex){ex.printStackTrace();}
}
void disp_Person()
{
System.out.print(id+" "+name+" ");
}
}
class Employee1 extends Person1 {
int sal;
String desgn;
void set_Emp(int id,String name,String desgn,int sal)
{
try{
set_Person(id,name);
this.desgn=desgn;
this.sal=sal;
}catch(Exception ex){ex.printStackTrace();}
}
void disp_Emp()
{
disp_Person();
System.out.print(desgn+" "+sal);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Employee1 e1=new Employee1();
e1.set_Emp(1001,"Manjeet","AP",20000);
e1.disp_Emp();
}
}
java中的继承类型
Java 在java中支持三种类型的继承:单级、多级和在类的情况下的分层继承,以避免歧义。
在 Java 编程中,仅通过接口支持多重继承和混合继承。
单继承示例
当一个类继承另一个类时,称为单继承。
class A
{
int a;
void set_A(int x)
{
a=x;
}
}
class B extends A{
int b,product;
void set_B(int x)
{
b=x;
}
void cal_Product()
{
product=a*b;
System.out.println("Product ="+product);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b=new B();
b.set_A(5);
b.set_B(5);
b.cal_Product();
}
}
多级继承示例
当存在继承链时,称为多级继承。
class A
{
int a;
void set_A(int x)
{
a=x;
}
}
class B extends A{
int b;
void set_B(int x)
{
b=x;
}
}
class C extends B{
int c,product;
void cal_Product()
{
product=a*b;
System.out.println("Product ="+product);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
C c=new C();
c.set_A(5);
c.set_B(5);
c.cal_Product();
}
}
层次继承示例
当两个或多个类继承一个类时,称为层次继承。
例如:
class A
{
int a;
void set_A(int x)
{
a=x;
}
}
class B extends A{
int b;
void set_B(int x)
{
b=x;
}
}
class C extends A{
int c;
void set_C(int x)
{
c=x;
}
// Java program to demonstrate inheritance in
// interfaces.
import java.io.*;
interface intfA {
void geekName();
}
interface intfB extends intfA {
void geekInstitute();
}
// class implements both interfaces and provides
// implementation to the method.
class sample implements intfB {
@Override public void geekName()
{
System.out.println("Rohit");
}
@Override public void geekInstitute()
{
System.out.println("JIIT");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
sample ob1 = new sample();
// calling the method implemented
// within the class.
ob1.geekName();
ob1.geekInstitute();
}
}
输出:
罗希特
JIIT
一个接口也可以扩展多个接口。
// Java program to demonstrate multiple inheritance
// in interfaces
import java.io.*;
interface intfA {
void geekName();
}
interface intfB {
void geekInstitute();
}
interface intfC extends intfA, intfB {
void geekBranch();
}
// class implements both interfaces and provides
// implementation to the method.
class sample implements intfC {
public void geekName() { System.out.println("Rohit"); }
public void geekInstitute()
{
System.out.println("JIIT");
}
public void geekBranch() { System.out.println("CSE"); }
public static void main(String[] args)
{
sample ob1 = new sample();
// calling the method implemented
// within the class.
ob1.geekName();
ob1.geekInstitute();
ob1.geekBranch();
}
}
输出
罗希特
JIIT
CSE
为什么Java中的类不支持多重继承,但通过接口可以实现?由于歧义,类不支持多重继承。在接口的情况下,没有歧义,因为方法的实现是由 Java 7 之前的实现类提供的。从 Java 8 开始,接口也有方法的实现。因此,如果一个类实现了两个或多个具有相同方法签名的接口,那么它也必须在类中实现该方法。
选你想看
你适合学Java吗?4大专业测评方法
代码逻辑 吸收能力 技术学习能力 综合素质
先测评确定适合在学习
在线申请免费测试名额
价值1998元实验班免费学
价值1998元实验班免费学













 在线咨询
在线咨询
 免费试学
免费试学